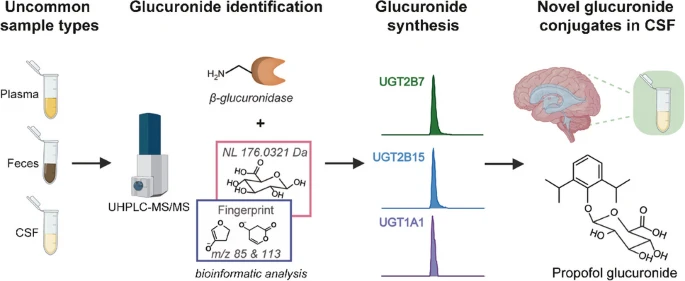
Glucuronidation is the major phase II biotransformation reaction that facilitates the clearance of exogenous compounds from the human body. Glucuronidated metabolites have been investigated in urine samples at a broad scale; however, their characterization in other human biospecimens is underexplored. Our study has now performed a comprehensive profiling of glucuronides in plasma, fecal, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of humans. We performed a mass spectrometry-based analysis that combines enzymatic hydrolysis with a β-glucuronidase to selectively cleave the glucuronic acid moiety, a developed in-house glucuronide identification pipeline, and enzymatic synthesis of standard metabolites. In total, we identified 32 glucuronidated metabolites across the three sample types in both negative and positive mass spectrometry ionization modes using advanced MS/MS fragmentation analysis. We have utilized a straightforward enzymatic synthesis of glucuronidated metabolites for annotation at the highest confidence level. Among the identified conjugates, we detected glucuronides of different compound classes including drugs, bile acid derivatives, steroid conjugates, and phenolic compounds. Unexpectedly, we validated the glucuronides of acetaminophen and propofol in CSF samples, the latter representing a novel observation that highlights the importance of investigating phase II metabolites in uncommon sample types.
Reference: Tsiara, I., Correia, M.S.P., Yang, F. et al. Global metabolomics profiling of glucuronides in human plasma, fecal, and cerebrospinal fluid samples. Anal Bioanal Chem (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-025-06082-w